Section 15.1: Double Integrals over rectangles
Example
EXAMPLE 2 If \(R = \{(x, y) | -1 \le x \le 1, -2 \le y \le 2\}\), evaluate the integral \(\iint_R \sqrt{1 - x^2} dA\).
EXAMPLE 2 If \(R = \{(x, y) | -1 \le x \le 1, -2 \le y \le 2\}\), evaluate the integral \(\iint_R \sqrt{1 - x^2} dA\).
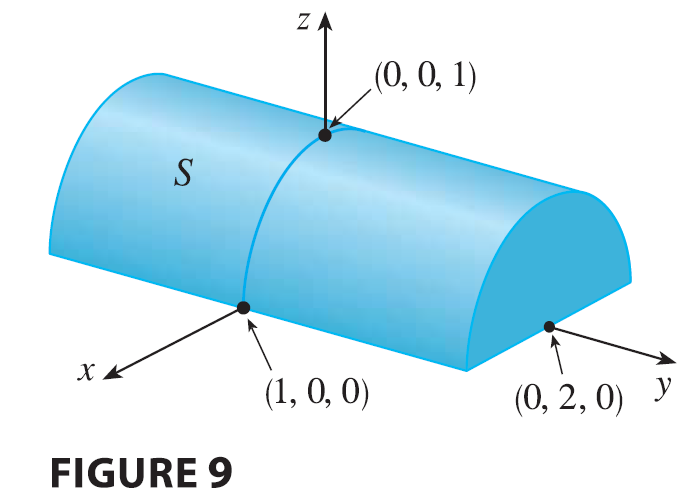
SOLUTION It would be very difficult to evaluate this integral directly from Definition 5 but, because \(\sqrt{1 - x^2} \ge 0\), we can compute the integral by interpreting it as a volume. If \(z = \sqrt{1 - x^2}\), then \(x^2 + z^2 = 1\) and \(z \ge 0\), so the given double integral represents the volume of the solid \(S\) that lies below the circular cylinder \(x^2 + z^2 = 1\) and above the rectangle \(R\). The volume of \(S\) is the area of a semicircle with radius 1 times the length of the cylinder. Thus \[ \iint_R \sqrt{1 - x^2} dA = \frac{1}{2}\pi(1)^2 \times 4 = 2\pi \]