Completion requirements
Equation of surfaces in Cylindrical Coordinates
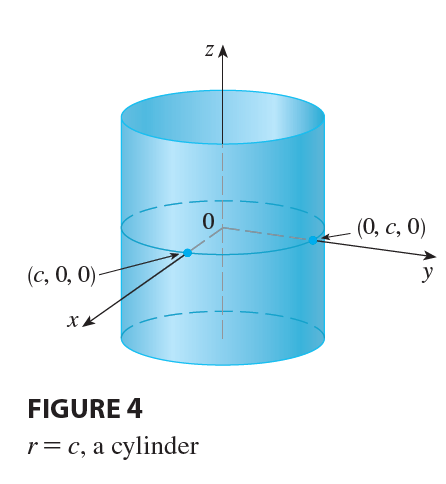
Cylindrical coordinates are useful in problems that involve symmetry about an axis, and the z-axis is chosen to coincide with this axis of symmetry. For instance, the axis of the circular cylinder with Cartesian equation \(x^2 + y^2 = c^2\) is the z-axis. In cylindrical coordinates this cylinder has the very simple equation \(r=c\). (See Figure 4.) This is the reason for the name “cylindrical” coordinates.
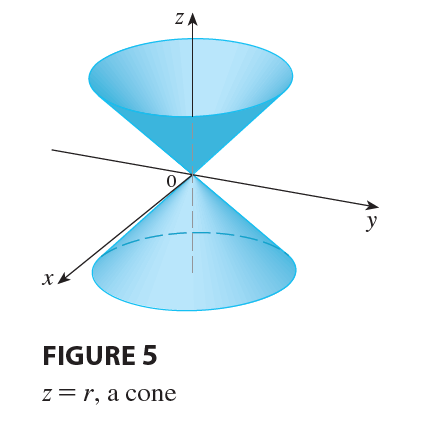
EXAMPLE 2 Describe the surface whose equation in cylindrical coordinates is \(z=r\).